Chinese hamster ovary cells in medicines: additional scientific information
CHO cells are derived from the epithelial cell line of the ovaries of the Chinese hamster. The Chinese hamster is a small rodent native to China and Mongolia.1
Due to their similarity to the human cell system, CHO cells are used to make therapeutic proteins in medicines such as biologics (also known as a biopharmaceuticals/biologicals/ group 2) and vaccines (group 3).2 Biologics are used to treat severe inflammatory diseases, autoimmune diseases, and some cancers.2 Biologics are made from living cells and include recombinant proteins, monoclonal antibodies, human growth hormones, cytokines, clotting factors.3
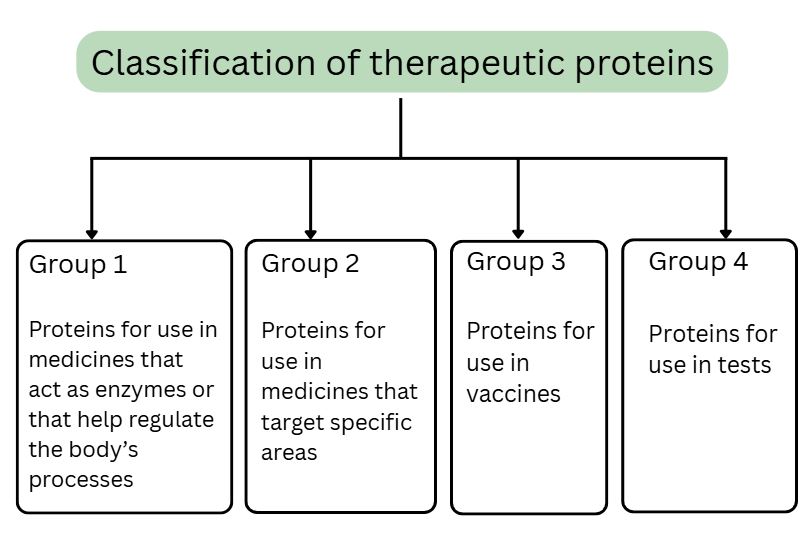
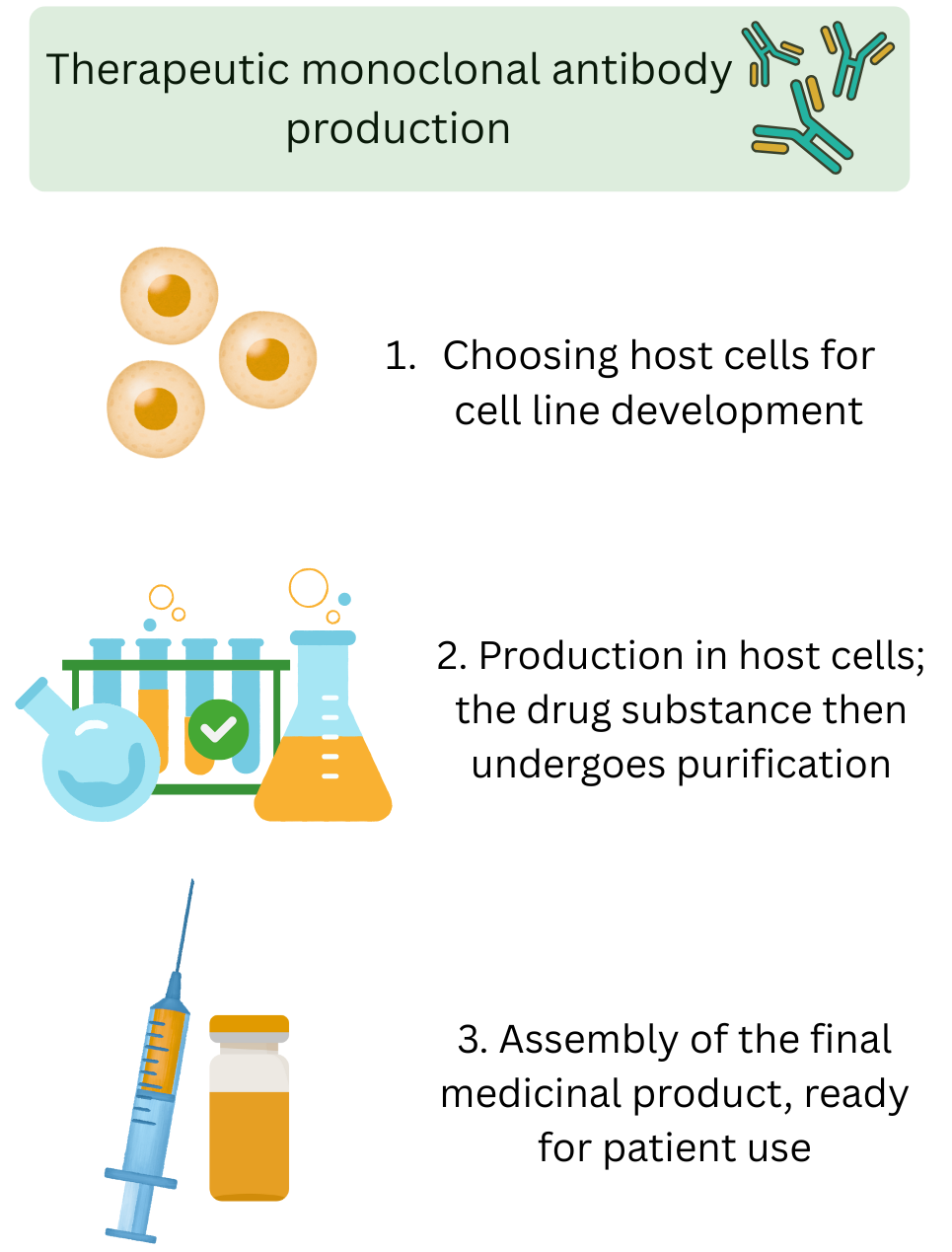
How medicines are made using CHO cells5
CHO cells are not used as an ingredient or excipient but they are used as host cells in the production of biologics and vaccines. The therapeutic proteins needed for biologics and vaccines are produced in the CHO host cells. Genes are inserted into the CHO cells and instruct them on how to make the protein. The protein is then extracted from the CHO cell and purified to make the medicine (biologics and vaccines).
<— go back to ‘Chinese hamster ovary cells in medicines’ page
References
- Evitria CHO cells – 7 facts about the cell line derived from the ovary of the Chinese hamster. Accessed 14.3.2025 from: https://www.evitria.com/journal/cho-cells/cho-cells/#:~:text=As%20the%20name%20suggests%2C%20Chinese,toxicity%20assays%20and%20gene%20expression. ↩︎
- Luther, E. (2025) Biological treatments, DermNet®. Available at: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/biologics (Accessed: 10 June 2025) ↩︎
- Glinšek, K., Bozovičar, K., & Bratkovič, T. (2023). CRISPR Technologies in Chinese Hamster Ovary Cell Line Engineering. International journal of molecular sciences, 24(9), 8144. Accessed: 10 June 2025. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098144 ↩︎
- Silpa S, Bertilla XJ, Rupachandra S. Emerging trends, challenges, and opportunities in protein therapeutics. In: Singh DB, Tripathi T, eds. Protein-Based Therapeutics. Singapore: Springer; 2023. doi:10.1007/978-981-19-8249-1_11 ↩︎
- Carrara SC, Ulitzka M, Grzeschik J, Kornmann H, Hock B, Kolmar H. From cell line development to the formulated drug product: the art of manufacturing therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Int J Pharm. 2021;594:120164. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.120164 ↩︎